The Role of Periodontists in Maintaining Gum Health
Gum health is important for overall oral health but is often ignored. Our gums support and protect our teeth by holding their sensitive roots and underlying bone structures in place. Periodontists are specialists who focus on keeping our gums and their supporting structures healthy. They are skilled at diagnosing, treating, and preventing gum diseases affecting oral health. Ensuring the importance of periodontal health is recognized helps maintain optimal oral health and overall well-being.
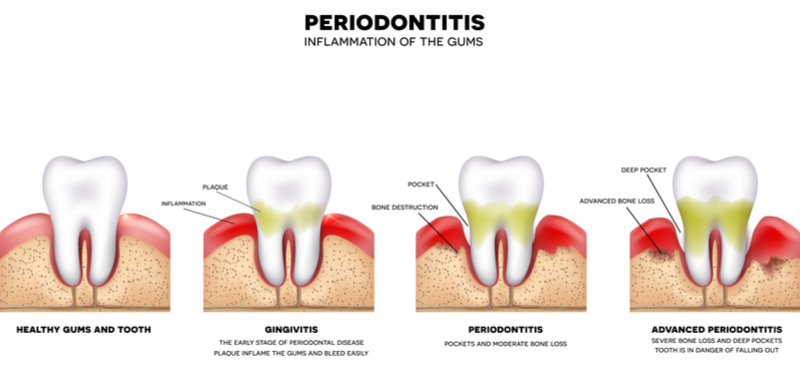
Understanding the Importance of Periodontal Health
Periodontal health includes the gums, surrounding tissues, and bone supporting the teeth. When these are healthy, they form a tight seal around the teeth, protecting them from harmful bacteria. However, gum disease can break this seal, causing inflammation, infection, and possibly tooth loss if not treated promptly.
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, is a widespread oral health problem. It usually starts as gingivitis, marked by red, swollen gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing. Good dental care and oral hygiene can reverse gingivitis. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can cause permanent damage to the gums and supporting bones.
The Role of Periodontists in Periodontal Health
Periodontists are dentists who have undergone additional years of specialized training in periodontology after completing dental school. This advanced training equips them with the knowledge and skills to diagnose, treat, and manage various stages of gum disease effectively. Here are key aspects of their role in maintaining gum health:
-
Diagnosis and Assessment:
Periodontists use special tools and methods to assess gum and support structural health. They measure pocket depths with probes and use dental X-rays to check bone levels, accurately diagnosing gum disease.
-
Treatment Planning:
A periodontist develops a treatment plan tailored to a patient’s needs based on their diagnosis. For patients with gingivitis, treatment may involve professional teeth cleaning (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gum line. In cases of periodontitis, more advanced treatments such as surgical procedures (e.g., flap surgery, gum grafting) may be necessary to restore gum health and prevent further damage.
-
Non-Surgical Treatments:
Periodontists usually begin with non-surgical treatments for gum disease. Scaling and root planing clean deeply beneath the gums, removing bacteria and smoothing tooth roots to help heal and prevent infection from coming back. They may also suggest medications or antimicrobial mouth rinses to improve treatment results.
-
Surgical Interventions:
When gum disease is severe or doesn’t improve with non-surgical treatments, periodontists perform surgery to reach deeper areas around tooth roots. Flap surgery lifts the gums to remove tartar and reduce pocket depths, making it easier to clean and maintain oral hygiene. Gum grafting may also be needed to cover exposed tooth roots and restore gum tissue lost due to disease. Therefore, surgical options become necessary for treating advanced gum issues effectively.
-
Maintenance and Follow-Up Care:
After initial treatment, periodontists stress the need for ongoing maintenance to prevent gum disease from coming back. They teach patients how to brush, floss, and use interdental cleaners properly to keep gums and teeth clean. Regular follow-up appointments help periodontists closely monitor gum health, adjust treatment plans as necessary, and promptly address any signs of disease recurrence. Therefore, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for long-term gum health.
-
Cosmetic Procedures for Periodontal Health:
When to See a Periodontist?
It’s advisable to consult a periodontist if you experience any signs of gum disease, such as:
- Persistent bad breath
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Gums receding or teeth fitting differently
Therefore, Periodontists play a vital role in maintaining gum health and preventing and treating gum disease. Their specialized training and expertise enable periodontists to provide comprehensive care that preserves gum integrity and supports long-term oral health. By seeking timely intervention and maintaining good dental hygiene habits, individuals can safeguard their smiles and enjoy the benefits of healthy gums for years to come.
For personalized guidance on maintaining your gum health or addressing any concerns related to gum disease, schedule a consultation with All Smiles Dental Clinic. To understand the importance of periodontal health, investing in your gum health today can contribute to a healthier, brighter smile tomorrow.
Leave a reply
Most Commented